Interface BodyTag
- All Superinterfaces:
IterationTag, JspTag, Tag
- All Known Implementing Classes:
BodyTagSupport
It is the responsibility of the tag handler to manipulate the body content. For example the tag handler may take the body content, convert it into a String using the bodyContent.getString method and then use it. Or the tag handler may take the body content and write it out into its enclosing JspWriter using the bodyContent.writeOut method.
A tag handler that implements BodyTag is treated as one that implements IterationTag, except that the doStartTag method can return SKIP_BODY, EVAL_BODY_INCLUDE or EVAL_BODY_BUFFERED.
If EVAL_BODY_INCLUDE is returned, then evaluation happens as in IterationTag.
If EVAL_BODY_BUFFERED is returned, then a BodyContent object will be created (by code generated by the JSP compiler) to capture the body evaluation. The code generated by the JSP compiler obtains the BodyContent object by calling the pushBody method of the current pageContext, which additionally has the effect of saving the previous out value. The page compiler returns this object by calling the popBody method of the PageContext class; the call also restores the value of out.
The interface provides one new property with a setter method and one new action method.
Properties
There is a new property: bodyContent, to contain the BodyContent object, where the JSP Page implementation object will place the evaluation (and reevaluation, if appropriate) of the body. The setter method (setBodyContent) will only be invoked if doStartTag() returns EVAL_BODY_BUFFERED and the corresponding action element does not have an empty body.
Methods
In addition to the setter method for the bodyContent property, there is a new action method: doInitBody(), which is invoked right after setBodyContent() and before the body evaluation. This method is only invoked if doStartTag() returns EVAL_BODY_BUFFERED.
Lifecycle
Lifecycle details are described by the transition diagram below. Exceptions that are thrown during the computation of doStartTag(), setBodyContent(), doInitBody(), BODY, doAfterBody() interrupt the execution sequence and are propagated up the stack, unless the tag handler implements the TryCatchFinally interface; see that interface for details.
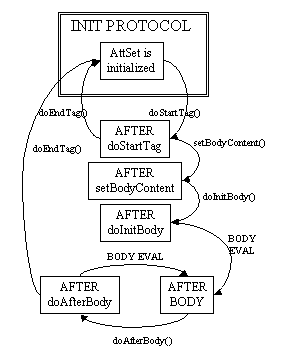
Empty and Non-Empty Action
If the TagLibraryDescriptor file indicates that the action must always have an empty element body, by a <body-content> entry of "empty", then the doStartTag() method must return SKIP_BODY. Otherwise, the doStartTag() method may return SKIP_BODY, EVAL_BODY_INCLUDE, or EVAL_BODY_BUFFERED.
Note that which methods are invoked after the doStartTag() depends on both the return value and on if the custom action element is empty or not in the JSP page, not how it's declared in the TLD.
If SKIP_BODY is returned the body is not evaluated, and doEndTag() is invoked.
If EVAL_BODY_INCLUDE is returned, and the custom action element is not empty, setBodyContent() is not invoked, doInitBody() is not invoked, the body is evaluated and "passed through" to the current out, doAfterBody() is invoked and then, after zero or more iterations, doEndTag() is invoked. If the custom action element is empty, only doStart() and doEndTag() are invoked.
If EVAL_BODY_BUFFERED is returned, and the custom action element is not empty, setBodyContent() is invoked, doInitBody() is invoked, the body is evaluated, doAfterBody() is invoked, and then, after zero or more iterations, doEndTag() is invoked. If the custom action element is empty, only doStart() and doEndTag() are invoked.
-
Field Summary
FieldsModifier and TypeFieldDescriptionstatic final intRequest the creation of new buffer, a BodyContent on which to evaluate the body of this tag.Fields inherited from interface IterationTag
EVAL_BODY_AGAINFields inherited from interface Tag
EVAL_BODY_INCLUDE, EVAL_PAGE, SKIP_BODY, SKIP_PAGE -
Method Summary
Modifier and TypeMethodDescriptionvoidPrepare for evaluation of the body.voidSet the bodyContent property.Methods inherited from interface IterationTag
doAfterBodyMethods inherited from interface Tag
doEndTag, doStartTag, getParent, release, setPageContext, setParent
-
Field Details
-
EVAL_BODY_BUFFERED
static final int EVAL_BODY_BUFFEREDRequest the creation of new buffer, a BodyContent on which to evaluate the body of this tag. Returned from doStartTag when it implements BodyTag. This is an illegal return value for doStartTag when the class does not implement BodyTag.- See Also:
-
-
Method Details
-
setBodyContent
Set the bodyContent property. This method is invoked by the JSP page implementation object at most once per action invocation. This method will be invoked before doInitBody. This method will not be invoked for empty tags or for non-empty tags whose doStartTag() method returns SKIP_BODY or EVAL_BODY_INCLUDE.When setBodyContent is invoked, the value of the implicit object out has already been changed in the pageContext object. The BodyContent object passed will have no data on it but may have been reused (and cleared) from some previous invocation.
The BodyContent object is available and with the appropriate content until after the invocation of the doEndTag method, at which case it may be reused.
- Parameters:
b- the BodyContent- See Also:
-
doInitBody
Prepare for evaluation of the body. This method is invoked by the JSP page implementation object after setBodyContent and before the first time the body is to be evaluated. This method will not be invoked for empty tags or for non-empty tags whose doStartTag() method returns SKIP_BODY or EVAL_BODY_INCLUDE.The JSP container will resynchronize the values of any AT_BEGIN and NESTED variables (defined by the associated TagExtraInfo or TLD) after the invocation of doInitBody().
- Throws:
JspException- if an error occurred while processing this tag- See Also:
-